
Why is this important?
With the ABSOLUTE-S protocol, surface and internal epitopes are preserved. Doing cell proliferation and protein analysis simultaneously is now much easier.

The growth of cells in the presence of 5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine (BrdUrd) has become an accepted method for monitoring DNA replication (1). The BrdUrd incorporation into the cellular DNA can be detected by reporter molecule labeled antibodies (2,3). The use of BrdUrd for assaying DNA replication is replacing methods utilizing radioisotope-labeled thymidine in both research and clinical laboratories. This assay is proving useful for the evaluation of tumor prognosis (4-7).
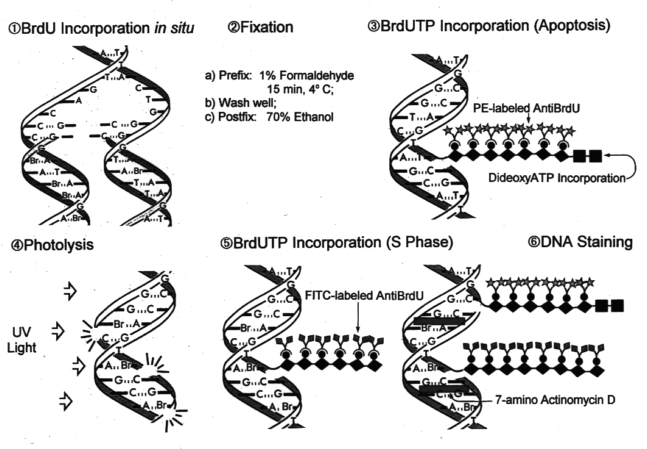
The incorporation of BrdUrd into cellular DNA is most commonly detected using anti-BrdUrd antibodies (1,2). This methodology although proven effective is limited when it comes to providing a complete analysis of the cells and/or tissues under investigation. This limitation arises as a result of the techniques required to make the incorporated BrdUrd available for measurement. It requires that the cellular DNA be denatured to separate the duplex strands in order for the BrdUrd epitope to become accessible and reactive to the antibody. This denaturation process usually involves either a heat treatment (>90C) or acid (2-4N HCl) treatment. The requirement for DNA denaturation results in the loss and/or extraction of many cellular proteins. This fact makes it difficult to combine additional simultaneous assays and probes for cell function and immunophenotyping when utilizing the heat/acid denaturation steps.
The strand break induced photolysis (SBIP) method utilized in the ABSOLUTE-S™ Kit does not require DNA denaturation and therefore is applicable in studies where preservation of antigens or other cellular features of the cells are desired. The SBIP method is based on the selective photolysis of DNA by ultraviolet (UV) light at sites of incorporation of BrdUrd. After photolysis of the DNA at the sites of BrdUrd incorporation, the UV-induced strand breaks are labeled with a modified deoxynucleotide triphosphate (Bromolated dUTP) by a reaction catalyzed by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT). The sites of BrdUTP incorporation into the DNA stand breaks are then identified with a reporter labeled anti-BrdUTP antibody (Fluorescein~PRB-1 antibody).
Link to ABSOLUTE-S assay flow diagram
By combining ABSOLUTE-S with the
APO-BRDU assay, it is possible to label proliferation and apoptosis simultaneously.
Reference: