| Eclipse CMV DNA Detection Kit | ||||||||||||
|
Introduction:
Kit
Features:
Summary and Explaination Human cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a DNA virus, approximately 200 nm in diameter, belonging to the herpes virus family. It has a double-stranded DNA core, a capsid and a surrounding envelope (1). Infection with CMV is common and is usually subclinical in the healthy host. However, CMV infection in the immuno-compromised host and the developing fetus may result in either localized or disseminated disease. Its clinical manifestations include pneumonia, retinitis, hepatitis, enteritis, and neurologic disease. Despite improved treatment modalities, CMV infection may result in significant morbidity and mortality in transplant patients, AIDS patients and cancer patients, particularly those with leukemia or lymphoma. Patients are at risk from both primary CMV infection and reactivation of latent infection (2-4). Early and rapid diagnosis of CMV infection is of great importance in avoiding over treatment with immunosuppressive drugs and in guiding antiviral therapy. However, distinguishing asymptomatic viral shedding from significant disease that requires treatment can be difficult. Isolation of CMV from blood specimens (Viremia) has been shown to correlate best with symptomatic disease, whereas isolation from saliva and urine are commonly found without apparent illness. Conventional methods for isolation of CMV from blood are sensitive, but may not yield results for several weeks. Shell vial cultures provide a result within 1 to 2 days, but are not sensitive for detection of CMV in blood specimens (5, 6). There are several requirements for an optimal assay for CMV monitoring. The most important characteristics are:
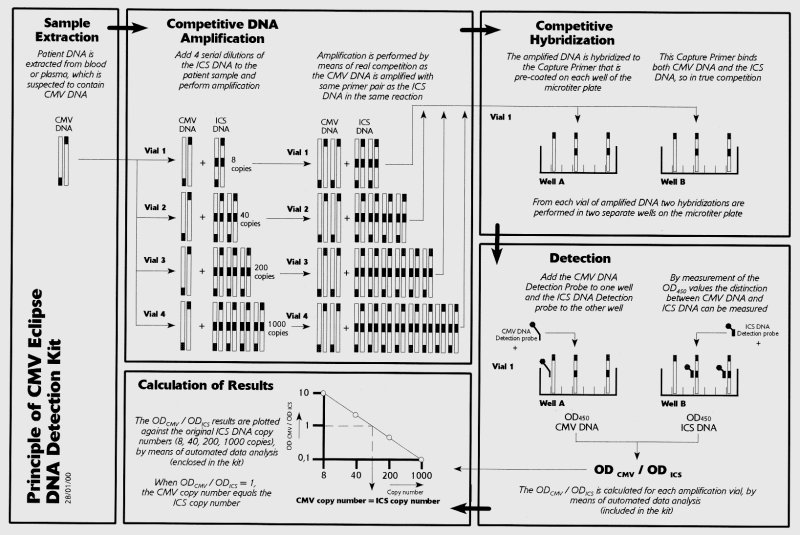
Until recently, rapid and reproducible quantitative results have been difficult to obtain. However, with the development of quantitative antigen detection methods, like the CMV antigenemia assay, and molecular amplification methods most of these requirements can now be obtained. The CMV antigenemia assay is valuable in the diagnosis and monitoring of active CMV infection in solid organ transplant patients and bone marrow transplant patients (1, 2, 7-11). Among the different methods for detecting CMV DNA or RNA, the PCR amplification system is mostly used for its sensitivity, specificity, reproducibility and potential to quantify (12-14). Studies involving PCR for the detection of CMV DNA (DNAemia) show that CMV is also detectable in a substantial number of patients with asymptomatic infection whom never progress to disease. However, patients with disease often have a higher viral load than those who remain asymptomatic (12). Principle of the Method The competitive PCR method is based on coamplification of known copy numbers of an exogenous DNA template, the Internal Competitive Standard (ICS) that competes with the target DNA for the same primers so that any variable affecting amplification has the same effect on both (15-18). The ICS used in this test is a homologous DNA competitor, with almost identical target sequence and amplification efficiency as the corresponding CMV IE-1 target. The constructed ICS contains PCR primer binding sites and a unique capture primer site identical to the CMV IE-1 target DNA, and a unique BIOprobe detection site that allows the resulting ICS PCR product to be distinguished from the CMV IE-1 PCR product. In the Eclipse CMV DNA Detection Kit, four different copy numbers of ICS are used in the amplification step to obtain an internal ICS reference line for the quantification of the unknown CMV DNA sample. The CMV primers provided in the Kit target a conserved DNA sequence of the IE-1 gene, whose protein product is present during the active CMV infection (19). During amplification both the target DNA and the ICS DNA compete for the available IE-1 specific primers. Following amplification, both ICS and IE-1 PCR products in the reaction mix are denatured and hybridized to CMV specific capture primers. Both ICS and target DNA will compete for the same CMV specific capture primers pre-bound to surface of the microwells. Competition for the same capture probe in the microwell during hybridization also ensures, that the obtained signal ratio always reflects the starting Target/Standard ratio. Two specific biotinylated detection primers are used separately to detect the ICS DNA or the CMV target DNA in the wells during hybridization. Following hybridization, the DNA products are detected by addition of a streptavidin-HRP conjugate and substrate. The signal generated by the enzym reaction is proportional to the amounts of ICS and CMV DNA products captured in the microwells. Since the ICS DNA is amplified at an efficiency identical to the CMV target DNA, and both the DNA products have the same binding capacity for the capture primer, the ICS reference line can serve as the standard for CMV target DNA quantification. Data analysis of the graph expressing the CMV OD450 signal/Standard OD450 signal ratio as a function of the Standard ICS copy number will give the input CMV target DNA copy number at the ratio of 1. In addition, the negative and positive control DNA samples in the Kit serve as controls for validation of each step during the test. The Eclipse CMV DNA Detection Kit is designed to amplify and detect CMV target DNA through the performance of 3 consecutive steps:
Principle of the Eclipse kit: In the below picture the complete principle of the Eclipse assay is explained. If you would like to receive a more clear picture by fax or mail, just let us know. Also if you have any questions, do not hesitate to let us know.
The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) process is covered by U.S. patents owned by Hoffmann-La Roche, Inc. and patents owned by F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
|
 |
   |
 |
|---|---|---|
| ||
 IQ Products
IQ Products