Back to apoptosis
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
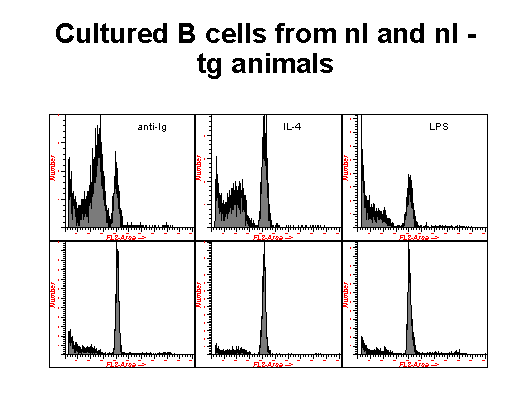
Another technique for the quantification of cells undergoing apoptosis is illustrated in these two pictures. In this method , the cells are fixed in ethanol and exposed to an extraction buffer and staining solution that facilitates the efflux of low molecular DNA that occurs in apoptotic cells as a result of the activation of an endonuclease which nicks DNA at internucleosomal sections. Thus cells that are revealed with DNA content less than that of G1 cells are identified as apototic. In these experiments, B cells from normal rats, rats transgenic for the bcl-2 proto-oncogene, XID rats and XID rats transgenic for bcl-2, were cultured with different immunomodulators and assayed for the induction of apoptosis. The top row of figure 1 represents normal B cells, the bottom row are the transgenic animals. In figure 2, the top row are XID cells with the bottom row representing XID animals with the transgene. As it has been reported, Bcl-2 falls into the category of apoptosis inhibitors and clearly protects the cells expressing this transgene from undergoing apoptosis when exposed to these immunomodulators . XID animals have an inherited immunodeficiency disorder.

 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
CD-ROM Vol 3 was produced by Monica M. Shively and other staff at the Purdue University Cytometry Laboratories and distributed free of charge as an educational service to the cytometry community. If you have any comments please direct them to Dr. J. Paul Robinson, Professor & Director, PUCL, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN 47907. Phone:(765) 494-0757; FAX (765) 494-0517; Web http://www.cyto.purdue.edu, EMAIL cdrom3@flowcyt.cyto.purdue.edu